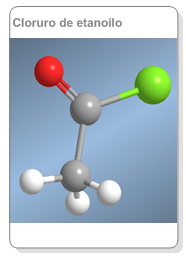
 Nomenclature of alkanoyl halides
Nomenclature of alkanoyl halides
They are named by changing the -oic acid ending to -oyl (ethanoyl chloride).
Reactivity of alkanoyl halides
It is the most reactive acid derivative towards nucleophilic attacks on the carbonyl group. The presence of the highly electronegative halogen positively polarizes the carbonyl carbon and facilitates the attack by nucleophiles.
Hydrolysis of alkanoyl halides
It hydrolyzes with water at room temperature and in the absence of catalysts, generating carboxylic acids.
Reaction with alcohols and amines
With alcohols, alkanoyl halides form esters. Their reaction with amines generates amides.
Reduction to alcohols and aldehydes
They are reduced to alcohols with lithium aluminum hydride. The reduction can be stopped at the aldehyde stage with modified reducing agents.
Reaction with organometallics
The reaction of alkanoyl halides with cuprates gives ketones. Grignard reagents can also be used at -78°C. Organolithium compounds react twice, forming alcohols.