 Nomenclature of amines
Nomenclature of amines
They are named by replacing the -o ending of the alkane with -amine (ethanamine).
Physical properties of amines
They are compounds with pyramidal geometry. They exhibit chirality although they are found as racemates. They form weaker hydrogen bonds than alcohols.
Acidity and basicity of amines
Amines behave as bases through the lone pair on the nitrogen. They also behave as weak acids and can be deprotonated using very strong bases (organolithiums).
Preparation of amines
Amines are obtained by the reduction of nitriles and amides with lithium aluminum hydride. The Hofmann rearrangement converts amides into amines with one less carbon. The reduction of azides allows for the preparation of amines with the same number of carbons as the starting haloalkane. The Gabriel synthesis allows for the preparation of amines from phthalic acid.
Hofmann and Cope Elimination
Amines can be converted into alkenes through Hofmann and Cope eliminations.
Mannich Reaction
The Mannich reaction leads to 3-aminocarbonyls from enolizable aldehydes or ketones, methanal, and primary or secondary amines.
Reaction of amines with nitrous acid
Reactions of amines with nitrous acid lead to the diazonium cation, which is very reactive. This reaction is of great interest with aromatic amines, as it allows for the introduction of a wide variety of groups onto benzene (Sandmeyer reactions).
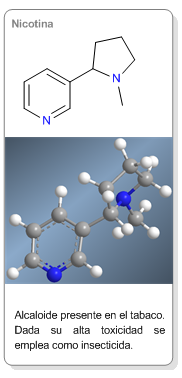
Learn more about amines........