 The allyl system: Stabilization by resonance
The allyl system: Stabilization by resonance
Allylic systems are stabilized by resonance. Positive charges, negative charges, and radicals are distributed equally between the two terminal carbons; this delocalization gives them significant stability.
SN2 in allylic systems
Allylic systems undergo SN2 reactions at a faster rate than normal systems.
SN1 in allylic systems
The SN1 reaction in these systems can occur even with primary haloalkanes. In these reactions, two types of products can be formed: kinetic and thermodynamic.
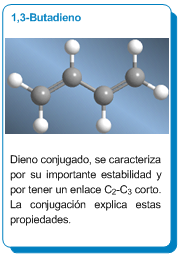
Conjugated dienes: 1,3-Butadiene
1,3-Butadiene is a conjugated diene; it exhibits special stability and a short C2-C3 bond distance due to orbital interaction.
Additions to conjugated dienes
Electrophilic additions to conjugated dienes form allylic cations that delocalize, leading to kinetic and thermodynamic products.
The thermodynamic product predominates at high temperatures and long reaction times. The kinetic product is mostly obtained under low temperature conditions and short reaction times.