 The Combustion Process
The Combustion Process
Combustion is a general process for all organic molecules, in which the carbon atoms of the molecule combine with oxygen to become molecules of carbon dioxide (CO2) and the hydrogen atoms to become liquid water (H2O). Combustion is an exothermic reaction, the released heat is called heat of combustion, and in many cases, it can be determined accurately, allowing the energy content of the molecules to be understood.
Balanced Combustion Reaction
![]()
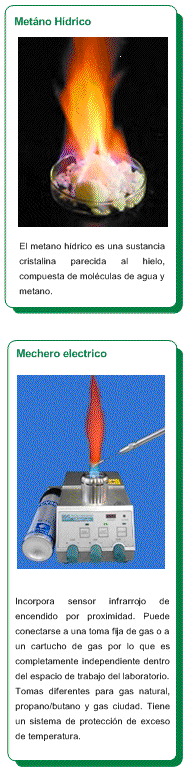
Stability of Isomers
Comparing the heats of combustion of isomeric alkanes shows that their values are not equal. For instance, 2-methylpropane releases -685.4 kcal/mol in its combustion, while butane releases -687.4 kcal/mol. These data demonstrate that butane has a higher energy content than 2-methylpropane and, therefore, is thermodynamically less stable.