¿Te cuesta entender la Química Orgánica?
¿Te cuesta entender la Química Orgánica?
Cursos de Química Orgánica para los Grados en Química, Ingeniería Química, Biotecnología y Farmacia de las Universidades españolas.
Material específico para cada Universidad con teoría, ejercicios y exámenes resueltos en vídeo, creado por Germán Fernández. Soporte para dudas por WhatsApp.
Más información en www.foroquimico.com
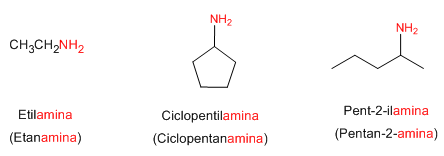
Regla 1. Las aminas se pueden nombrar como derivados de alquilaminas o alcanoaminas. Veamos algunos ejemplos.
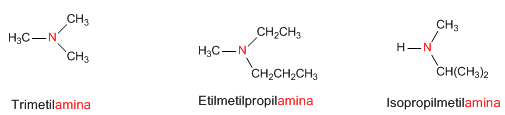
Regla 2. Si un radical está repetido varias veces, se indica con los prefijos di-, tri-,...
Si la amina lleva radicales diferentes, se nombran alfabéticamente.
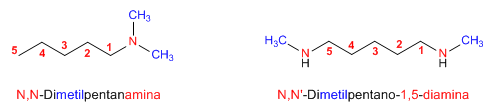
Regla 3. Los sustituyentes unidos directamente al nitrógeno llevan el localizador N. Si en la molécula hay dos grupos amino sustituidos se emplea N,N'.
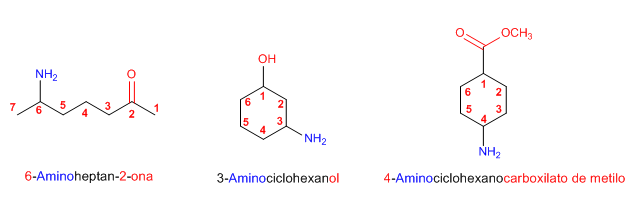
Regla 4. Cuando la amina no es el grupo funcional pasa a nombrarse como amino-. La mayor parte de los grupos funcionales tienen prioridad sobre la amina (ácidos y derivados, carbonilos, alcoholes)