¿Te cuesta entender la Química Orgánica?
¿Te cuesta entender la Química Orgánica?
Cursos de Química Orgánica para los Grados en Química, Ingeniería Química, Biotecnología y Farmacia de las Universidades españolas.
Material específico para cada Universidad con teoría, ejercicios y exámenes resueltos en vídeo, creado por Germán Fernández. Soporte para dudas por WhatsApp.
Más información en www.foroquimico.com
Regla 1. Los ésteres proceden de condensar ácidos con alcoholes y se nombran como sáles del ácido del que provienen. La nomenclatura IUPAC cambia la terminación -oico del ácido por -oato, terminando con el nombre del grupo alquilo unido al oxígeno.
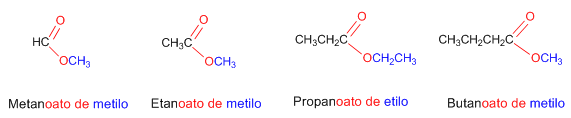
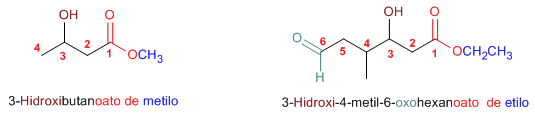
Regla 2. Los esteres son grupos prioritarios frente a aminas, alcoholes, cetonas, aldehídos, nitrilos, amidas y haluros de alcanoilo. Estos grupos se nombran como sustituyentes siendo el éster el grupo funcional.
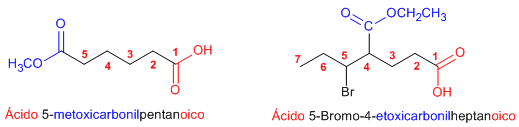
Regla 3. Ácidos carboxílicos y anhídridos tienen prioridad sobre los ésteres, que pasan a nombrarse como sustituyentes (alcoxicarbonil......)
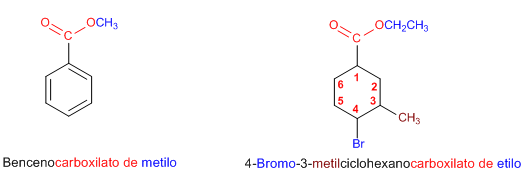
Regla 4. Cuando el grupo éster va unido a un ciclo, se nombra el ciclo como cadena principal y se emplea la terminación -carboxilato de alquilo para nombrar el éster.