Halogenation of Methane: Global Reaction
The halogenation of methane is a reaction that proceeds with the formation of free radicals and takes place in three stages.
![]()

Initiation Stage
In the first step of the reaction, the homolytic cleavage of the Cl-Cl bond occurs. This is achieved with heat or by absorbing light.
![]()
First Propagation Stage
This is a slightly endothermic stage that involves the abstraction of a hydrogen atom from methane by the chlorine radical formed in the previous stage, generating the methyl radical.
![]()
Second Propagation Stage
During this stage, the methyl radical abstracts a chlorine atom from one of the initial molecules, producing chloromethane and a new chlorine atom. This chlorine atom returns to the first propagation stage, and the whole process repeats.
![]()
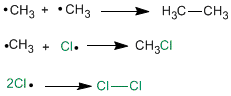
Termination Stage
This occurs when the reactants are exhausted, and the radicals in the medium combine with each other.