Rule 1. In monosubstituted benzenes, the substituent is named first, followed by the word "benzene."
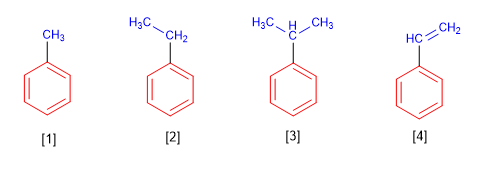
[1] Methylbenzene (Toluene)
[2] Ethylbenzene
[3] Isopropylbenzene
[4] Vinylbenzene (Styrene)
Rule 2. In disubstituted benzenes, the position of the substituents is indicated using the prefixes ortho- (o-), meta- (m-) and para- (p-). Number locators 1,2-, 1,3- and 1,4- can also be used.
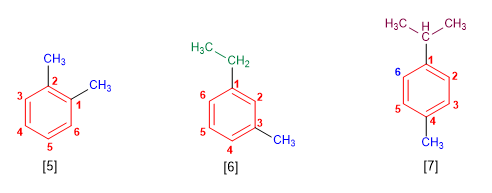
[5] 1,2-Dimethylbenzene (o-Dimethylbenzene)
[6] 1-Ethyl-3-Methylbenzene (m-ethylmethylbenzene)
[7] 1-Isopropyl-4-methylbenzene (p-isopropylmethylbenzene)
Disubstituted derivatives can be named using the particles ortho-, meta-, para.
Rule 3. In benzenes with more than two substituents, the ring is numbered so that the substituents take the lowest locators. If several numbering schemes give the same locators, preference is given to alphabetical order.
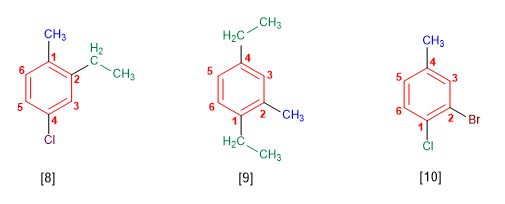
[8] 4-Chloro-2-ethyl-1-methylbenzene
[9] 1,4-Diethyl-2-methylbenzene
[10] 2-Bromo-1-chloro-4-methylbenzene
Rule 4. There are numerous derivatives of benzene with common names that are useful to know:
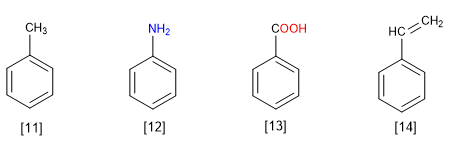
[11] Toluene
[12] Aniline
[13] Benzoic Acid
[14] Styrene
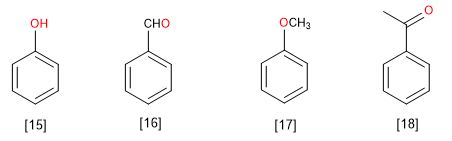
[15] Phenol
[16] Benzaldehyde
[17] Anisole
[18] Acetophenone
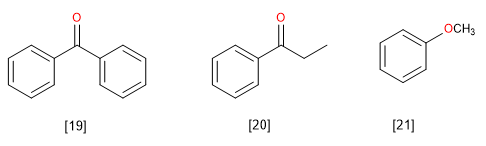
[19] Benzophenone
[20] Propiophenone
[21] Anisole